Toenails, often taken for granted, play an essential role in protecting the sensitive tips of our toes. However, when toenails become sick, inflamed, or infected, they can cause significant discomfort and distress. A variety of factors can contribute to toenail issues, ranging from fungal infections to trauma or even systemic health problems. Understanding the underlying causes, symptoms, and treatment options is key to maintaining healthy, pain-free feet.
Common Causes of Inflamed Toenails
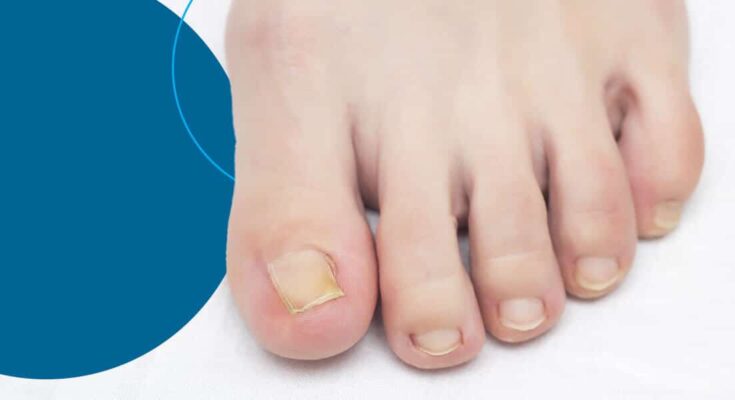
- Fungal Infections (Onychomycosis) One of the most common causes of inflamed toenails is a fungal infection, which affects the toenail’s appearance, causing it to become discolored, thickened, or brittle. Fungal infections thrive in warm, moist environments like shoes and socks, making the toenails especially susceptible.
- Ingrown Toenails An ingrown toenail occurs when the edge of the nail grows into the surrounding skin, leading to pain, redness, and swelling. If left untreated, this can lead to infections and even require surgical intervention. Tight shoes or improper nail trimming are common causes of this condition.
- Trauma or Injury Dropping something heavy on your toe, stubbing it, or even repetitive pressure from ill-fitting shoes can cause damage to the toenail and surrounding tissue. This injury can result in inflammation, bruising, and potential nail loss.
- Paronychia Paronychia is a bacterial or fungal infection of the skin around the nail. It often occurs after a hangnail, cut, or other injury to the area. Symptoms include redness, swelling, and sometimes pus formation around the nail.
- Psoriasis and Other Skin Conditions Psoriasis, a chronic autoimmune condition, can also affect the toenails, causing them to become thick, pitted, or discolored. Other skin conditions like eczema may also lead to toenail inflammation.
- Poor Nail Hygiene Poor hygiene practices, such as not trimming nails properly or failing to dry feet thoroughly, can increase the risk of fungal or bacterial infections that lead to inflammation.
Symptoms to Watch For
The symptoms of inflamed toenails can vary depending on the underlying cause, but common signs include:
- Redness and Swelling: The area around the toenail may become inflamed, making the toe appear swollen and tender to the touch.
- Pain or Tenderness: You may experience pain when walking, touching, or putting pressure on the affected toe.
- Discoloration: Infected nails may appear yellow, brown, or greenish, depending on the type of infection.
- Thickening or Brittle Nails: Fungal infections and psoriasis often lead to toenails becoming thick, rough, or brittle.
- Pus or Drainage: If the inflammation is due to an infection, pus or fluid may drain from the area around the nail.
Treatment Options for Inflamed Toenails
The treatment for an inflamed toenail depends on its cause. Here are some general approaches:
- For Fungal Infections:
- Topical Antifungal Medications: Over-the-counter antifungal creams, sprays, or lacquers can be effective for mild fungal infections.
- Oral Antifungals: For more severe cases, oral antifungal medications may be necessary. These drugs can help eliminate the infection from within.
- Laser Therapy: In some cases, laser treatments may be used to target and destroy the fungus.
- For Ingrown Toenails:
- Proper Nail Trimming: Trim your nails straight across to prevent them from growing into the skin.
- Soaking the Foot: Warm water soaks can help soften the toenail and reduce swelling. Epsom salts may be added to relieve discomfort.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases, a podiatrist may need to remove a portion of the toenail or the entire nail to promote healing.
- For Trauma or Injury:
- Rest and Elevation: Reducing pressure on the affected toe can help reduce swelling.
- Cold Compress: Applying ice wrapped in a cloth can reduce swelling and ease pain.
- Antibiotics: If an infection develops, a healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics to treat the infection.
- For Paronychia:
- Soaking the Toe: Soak the toe in warm, soapy water to reduce swelling and soften the tissue.
- Topical Antibiotics: If bacterial, topical antibiotics like Neosporin can help prevent infection from worsening.
- Drainage: If an abscess forms, a doctor may need to drain it to release the pus and reduce inflammation.
- For Psoriasis:
- Topical Treatments: Steroid creams or topical vitamin D analogs may help reduce inflammation associated with psoriasis.
- Systemic Medications: For severe psoriasis, oral or injectable biologic medications may be prescribed to control the condition.
Preventing Toenail Inflammation
Preventing toenail inflammation involves adopting healthy habits:
- Wear Proper-Fitting Shoes: Shoes that are too tight or too loose can cause trauma to the toenails or create an environment conducive to fungal growth.
- Trim Nails Regularly and Correctly: Trim your toenails straight across to avoid ingrown toenails.
- Practice Good Foot Hygiene: Wash and dry your feet regularly, especially if you sweat a lot. Consider using foot powder to reduce moisture buildup.
- Avoid Walking Barefoot in Public Areas: Areas like locker rooms or pools are breeding grounds for fungi that can cause infections.
- Moisturize Your Feet: Keeping your feet hydrated can prevent cracks and fissures that allow infections to enter.
Final
Toenail inflammation is a common issue, but it’s also highly treatable when addressed early. Whether due to fungal infections, ingrown nails, trauma, or skin conditions, understanding the cause of your inflamed toenails is essential for effective treatment. By adopting good foot hygiene, wearing the right footwear, and seeking timely medical attention when needed, you can keep your toenails healthy and free from inflammation. If the problem persists or worsens, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider or podiatrist for personalized advice and treatment.